 Traffic Topology
Traffic Topology
This document was translated by ChatGPT
#1. Traffic Topology
DeepFlow's traffic topology is used to display the dependencies between services or resources, facilitating better analysis and problem-solving, such as analyzing performance bottlenecks, single points of failure, or potential dependency access issues.
#1.1 Overview
00-Overview
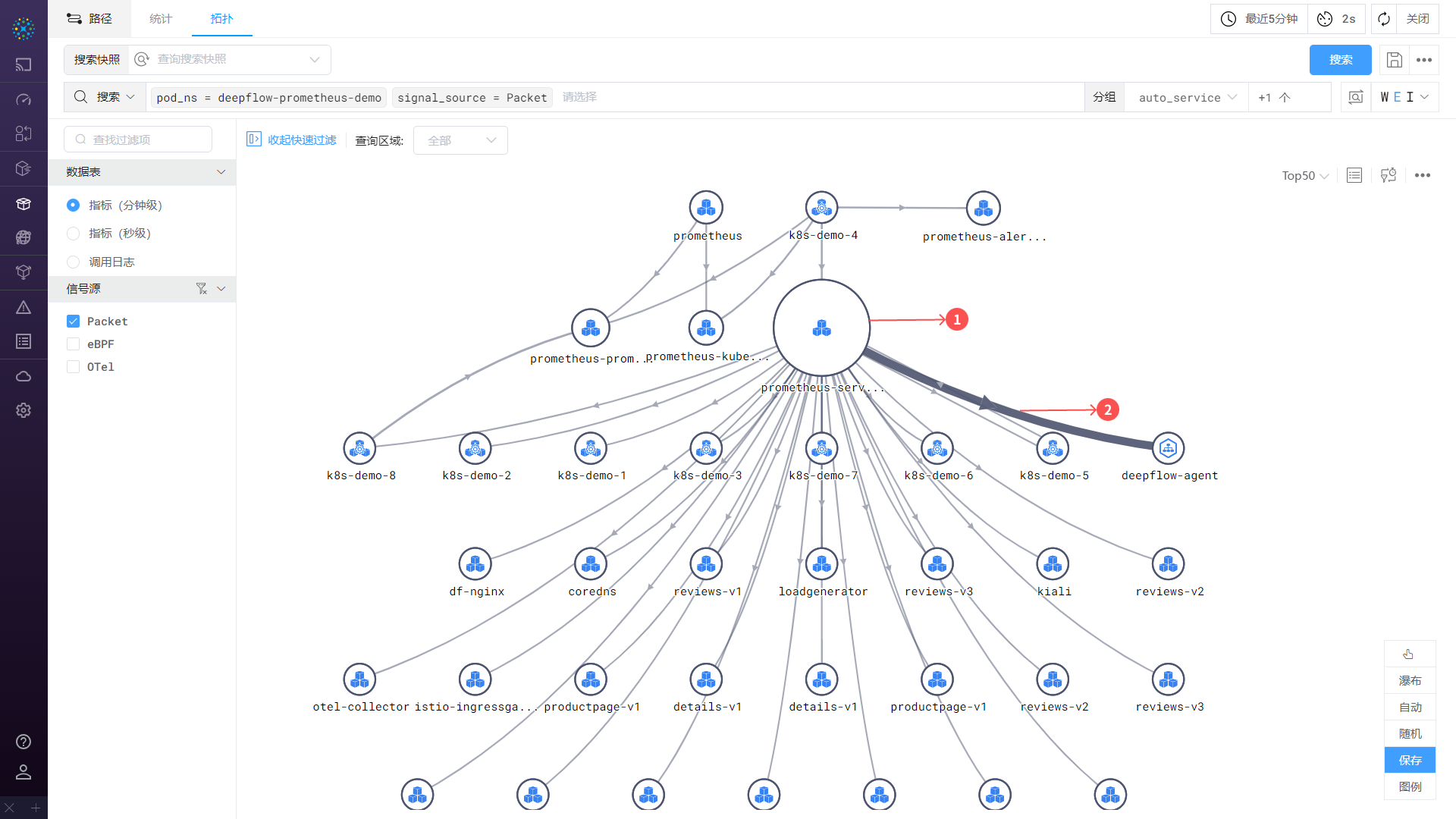
The traffic topology consists of nodes, paths, and some operations:
- ① Node: Represents a service or resource, corresponding to the
groupin the search criteria. It can be a container service, cloud server, or region, etc. - ② Path: Represents the direction of service or resource, where the
clientaccesses theserver. - Operations: You can hover over or click on
nodesorpaths.- Hover: Highlight the
nodeorpathto view metrics. - Click: View details of the
nodeorpathin a right-slide frame.
- Hover: Highlight the
#1.1.1 Topology Details
01-Topology
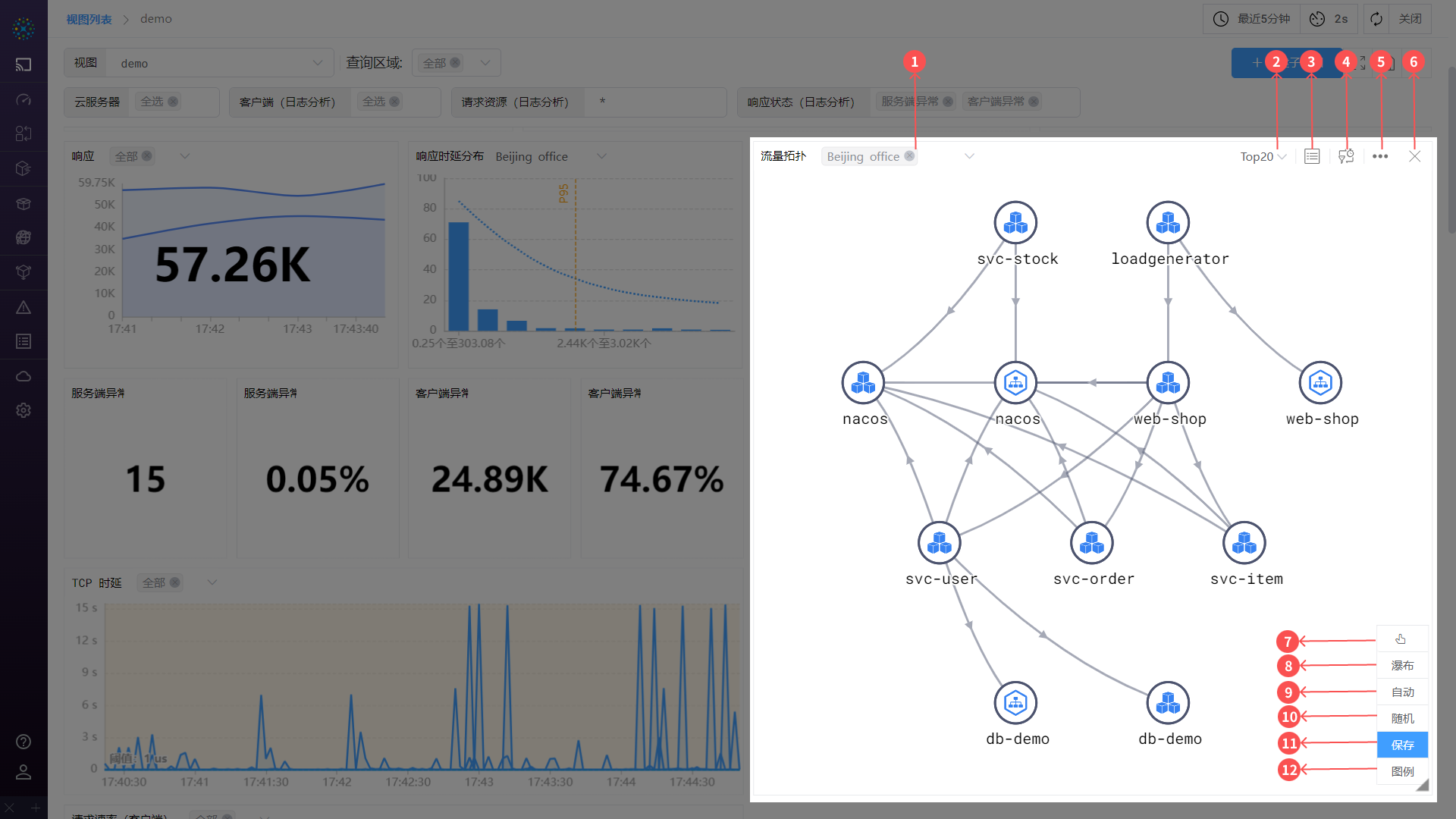
- ① Switch Query Area: If there are multiple storage areas in the previous data, you can quickly switch areas for data queries.
- Note: If the query criteria are not grouped, there is no
Switch TOP Datafunction.
- Note: If the query criteria are not grouped, there is no
- ② Switch Top Data: Sort the main metric values of the nodes in descending order based on the grouping.
- Note: If the query criteria are not grouped, there is no
Switch TOP Datafunction.
- Note: If the query criteria are not grouped, there is no
- ③ Expand Table: Click to expand or close the table. For details, please refer to the [Expand Table] section.
- ④ Modify Metrics: You can modify the metrics. For details, please refer to the [Modify Metrics] section.
- ⑤ Settings: Click to set the
traffic topology. For details, please refer to the [Settings] section. - ⑥ Delete: This is a
Dashboardcapability. If you do not need to display thistraffic topologyin the Dashboard, you can click the delete button to remove it. - ⑦ Manually Supplement Resource Relationship Mode: In this mode, you can manually add paths between nodes.
- ⑧ Waterfall/Free Topology: Supports switching the display form of the topology. Free topology is generally used for scenarios with many nodes and complex paths; waterfall topology is generally used for scenarios with fewer nodes and simpler paths.
- ⑨ Auto Layout: The system arranges the nodes in a tree structure based on the path access relationships.
- ⑩ Random Layout: The system arranges the nodes in a star structure.
- ⑪ Save Topology: This is a
Dashboardcapability. After modifying thetraffic topology, you can choose theSave Topologybutton to save the changes, such as remembering the time range, topology position, topology configuration, and variable template values. - ⑫ Legend: You can open the legend to view the meanings of icons and lines. For details, please refer to the [Legend] section.
#1.1.2 Hover TIP

02-Hover TIP
When the mouse hovers over a node, the path associated with the node is automatically highlighted. When hovering over a path, the nodes associated with the path are automatically highlighted. At the same time, you can view the metrics in the form of a TIP, which can display the metrics corresponding to different observation points.
#1.1.3 Hover Display Metrics

03-Hover Display
Taking the mouse hovering over a path as an example, the TIP display content is introduced.
- The first row: Explanation and legend display area. The legend explanation is as follows:
- Application Function
- A Application: Represents metrics obtained through application instrumentation, currently indicating data with
signal source=OTel. - S System: Represents metrics obtained through eBPF, currently indicating data with
signal source=eBPF. - E Endpoint Network: Represents metrics obtained through traffic capture (BPF), currently indicating data collected from the network card of the client or server.
- M Middle Network: Represents metrics obtained through traffic capture (BPF), currently indicating data collected from locations other than the network card of the client or server.
- A Application: Represents metrics obtained through application instrumentation, currently indicating data with
- Network Function: All metrics are obtained from traffic capture (BPF).
- D Network Card: Indicates data collected from the network card of the client or server.
- K Container Node: Indicates data collected from the network card of the container node.
- H Host: Indicates data collected from the network card of the host.
- M Middle Network: Indicates data collected from locations other than the above network cards.
- Corner Mark: Distinguishes whether the current data collection location is on the client or server.
- C: Represents the client.
- S: Represents the server.
- Application Function
- The second row: Hover
node/pathname information. - Others: Metrics display area.
- Displays the relevant metric values based on the data location.
- The last column shows the difference of all
observation points, which can quickly determine if there is data inconsistency insent traffic. - Example: As shown in the figure below, it indicates the endpoint network data of the client.

04-Icon
#1.1.4 Settings
Users can click the gear icon to set the traffic topology.

05-Settings
- Display Full Name: Display the full name of the node or the default display.
- Download CSV Data: Supports downloading the data information of the
traffic topology. - View API: View the interface information that generates the
traffic topology.
#1.1.5 Expand Table
Click the Expand Table button to display the metrics of nodes and paths in the traffic topology in a list form, including resource monitoring, path monitoring, and path difference tables.

06-Table
- Resource Monitoring: Displays the metrics of all nodes in the
traffic topology. - Path Monitoring: Displays the metrics of all paths in the
traffic topology. - Path Difference: Displays the difference in metrics of all paths in the
traffic topologyat differentobservation points. - Search: Supports quick search and lookup of table data.
- Settings: Set the display method of column width, such as evenly distributing column width or allocating column width according to content.
#1.1.6 Modify Metrics
Metrics are one of the important components of the chart. DeepFlow provides a shortcut to help users quickly select metrics. You can choose the metrics to be displayed in the dropdown menu.

07-Modify Metrics
- ① Metric Name: Select the metric name to display the metric data in the chart.
- ② Set as Main Metric: Click the icon to set the metric as the main metric. When
Switching TOP Data, the chart is sorted by the main metric value. - ③ Advanced Settings: You can add, delete, or modify metrics. For details, please refer to the [Advanced Settings] section.
- Multi-select/Single-select: Supported by some charts. In
multi-select, the TIP in the chart can display multiple metrics. Insingle-select, only one metric can be displayed.
#1.1.7 Advanced Settings
For further settings of metrics, you can click Modify Metrics -> Advanced Settings to enter the settings page. As shown in the figure below, it supports users to add or delete metrics, add aggregation functions, modify display names, set thresholds, select metric templates, and other operations.

08-Advanced Settings
- ① Select Template: Select
metric templateto quickly switch the metric template in the current popup window. - ② One-click Clear: One-click clear all metrics in the current popup window.
- ③ Save Template: Save the settings state of the metrics in the current popup window as a
metric template. - ④ Metric Column: Click the input box to pop up the dropdown box, and you can select metrics according to the classification.
- Aggregation - Primary Operator: Perform function aggregation operations on metrics, supporting functions such as average, sum, maximum, minimum, etc.
- Aggregation - Secondary Operator: Perform secondary calculations based on the data obtained by the
primary operator. - Name: Set the display name of the metric.
- Unit: Set the display unit of the metric.
- Threshold: Set the threshold of the metric. When the threshold is exceeded, the
nodeorpathwill turn red to prompt.
- ⑤ Enable/Disable Metrics: Show/hide the corresponding metrics.
- ⑥ Add Metrics: Add
④ Metric Columnin the current popup window.
#1.1.8 Edit
The topology edit box consists of three parts: ① Chart, ② Search Criteria, and ③ Style and Settings.

09-Edit
- ① Chart: The chart is drawn based on
② Search Criteriaand③ Style and Settings. - ② Search Criteria: For the use of search criteria, please refer to the Search section.
- ③ Style and Settings: Set the style, color, and other settings of the chart.
- Style: Rich functions support setting the style of the chart.
- Title: Supports modifying the chart name.
- Chart Style:
- Full Name Display: Full name display/abbreviated display of node names.
- Display Main Metric: When enabled, the main metric value will be displayed on the path.
- Close Thumbnail: Supports enabling/disabling the thumbnail.
- Turning Point of Step Line Chart: Supports setting the position of the data turning point.
- Area Fill: Supports filling the area between the line and the coordinate axis with color.
- Data Stacking: Supports displaying multiple data series in a stacked or tiled manner.
- Stacking: Displays the values of multiple data series in the same coordinate system in a stacked manner to show their overall trend and respective contributions.
- Tiling: Displays the values of multiple data series in the same coordinate system in a tiled manner to better show the differences and relationships between them.
- Color: Supports setting the color of paths and nodes.
- Style: Rich functions support setting the style of the chart.
#1.1.9 Legend
Click Legend to view the meanings of icons and lines.

10-Legend


